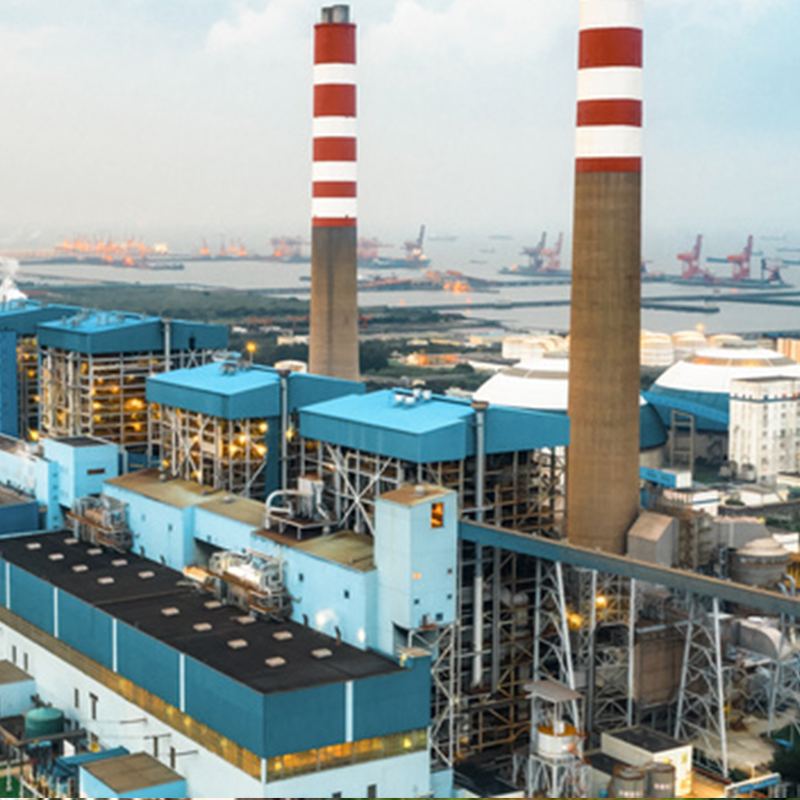
Understanding Gas Desulfurization: A Pathway to Sustainability
Gas desulfurization refers to the process of removing sulfur compounds, primarily sulfur dioxide (SO2), from gas streams in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical manufacturing. This crucial technique involves the use of various methods, including wet and dry scrubber technologies, to minimize the release of harmful sulfur oxides into the atmosphere. By targeting and treating exhaust gases, gas desulfurization ensures that industries can reduce their environmental impact and comply with stringent regulations aimed at minimizing air pollution.
The importance of gas desulfurization in modern industry cannot be overstated, particularly regarding its contributions to reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide. According to data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, sulfur dioxide emissions from power plants decreased by 92% between 1995 and 2021. This substantial reduction is a direct outcome of implementing gas desulfurization technologies, which play a pivotal role in achieving sustainable development goals. Furthermore, by lowering the release of sulfur compounds, these practices help decrease acid rain formation and improve air quality, thereby fostering a more sustainable future for both the environment and human health.
Benefits of Gas Desulfurization for Sustainability
Gas desulfurization plays a crucial role in reducing air pollution by significantly lowering sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, contributing immensely to cleaner air. Sulfur oxides, primarily produced by burning fossil fuels, can lead to acid rain and have detrimental effects on the environment and human health. Implementing desulfurization technologies can result in a substantial decrease in these pollutants. For instance, SO2 emissions from U.S. power plants decreased by 92% from 1995 to 2021, as per data from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This reduction highlights the positive impact such technologies have on improving air quality and supporting the broader environmental goal of cleaner air.
From an economic perspective, gas desulfurization technologies contribute significant cost savings by helping companies comply with environmental regulations and avoid substantial fines. These benefits are not just short-term; by adhering to sustainable practices, companies can achieve long-term financial gains. For example, the implementation of flue gas desulfurization systems often leads to the creation of valuable byproducts, such as gypsum, which can be used in construction, thus offering another revenue stream. Moreover, sustainability-driven transformations often improve Company reputations, attracting environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
Furthermore, gas desulfurization ensures companies meet stringent emissions standards imposed by environmental authorities like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Compliance with such regulations prevents the imposition of penalties, while simultaneously enhancing corporate social responsibility and promoting sustainable industry practices. By investing in advanced desulfurization technologies, companies position themselves as leaders in the drive towards sustainability, setting benchmarks for industry-wide environmental responsibility and aligning with global sustainability targets.
Technologies Employed in Gas Desulfurization Processes
Gas desulfurization involves several advanced technologies that have been developed to effectively remove sulfur compounds from industrial emissions. Wet scrubbing techniques are prevalent in power plants and industrial facilities. These methods typically use chemical solvents, such as limestone slurry, to absorb sulfur dioxide from flue gases. The process is highly efficient in environments where large-scale emissions need to be controlled, as evidenced by its successful application in numerous power and chemical processing plants.
Dry scrubbing methods, on the other hand, utilize solid sorbent materials to capture sulfur compounds. These techniques are particularly advantageous in situations where water use is a concern or where operational simplicity is desired. Dry scrubbing is often preferred in smaller facilities or those looking to minimize water consumption, offering flexibility and ease of implementation while maintaining effectiveness in sulfur removal.
Recent innovations in flue gas desulfurization technology have significantly improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Advances in catalytic processes and the integration of online monitoring systems have revolutionized the sector. These technologies enhance the precision of pollutant removal and enable real-time adjustments to desulfurization operations, therefore reducing downtime and operational costs. This progress ensures that industries can meet stringent environmental regulations while optimizing performance levels.
Challenges Faced in Gas Desulfurization Implementation
Implementing gas desulfurization systems is associated with high installation and operational costs, which pose a significant challenge for industries. The initial cost entails substantial capital investment, often running into millions of dollars for large-scale facilities. Ongoing operational expenses, such as continuous maintenance and energy consumption, add to the financial burden, especially for existing facilities that require upgrades to integrate these systems. For instance, flue gas desulfurization setups in power plants demand considerable resources for both installation and sustained operation.
Technological complexities further complicate the implementation of gas desulfurization systems. Integrating these systems into existing operations demands not only advanced engineering solutions but also continuous maintenance to ensure their efficiency. Regular maintenance is crucial to avoid disruptions, and this requires skilled personnel capable of handling sophisticated equipment and technology. The ability to troubleshoot and optimize these systems is paramount to successful implementation, making personnel training a vital component of the process.
Regulatory and environmental challenges also play a critical role in the deployment of gas desulfurization technologies. With strict regulations and environmental standards constantly evolving, industries must continually adapt their systems to remain compliant. These legislative changes often necessitate system upgrades to meet new criteria, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Moreover, regulatory compliance involves navigating potential operational hurdles, such as obtaining permits and aligning technological capabilities with environmental targets, ensuring industries can meet both current and future requirements.
Real-World Applications of Gas Desulfurization
Gas desulfurization plays a critical role in power generation, especially in coal-fired plants. These plants have traditionally been significant sources of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, contributing to acid rain and respiratory problems. With stricter regulations, coal-fired plants have adopted gas desulfurization technologies to meet environmental standards and reduce emissions. For instance, flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems allow these plants to minimize their SO2 output significantly, thus making a substantial impact on improving air quality and public health.
In chemical processing plants, gas desulfurization has been instrumental in mitigating sulfur emissions. These facilities often release SO2 as a byproduct, which can harm the environment and human health. By integrating desulfurization technologies into their processes, chemical plants can effectively trap and neutralize harmful emissions, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. This integration not only supports environmental protection but also enhances the operational efficiency and sustainability of chemical production lines.
The cement and steel industries are also pivotal adopters of gas desulfurization technologies. In these sectors, desulfurization processes are implemented to curtail SO2 emissions and reduce their environmental footprint. By employing such technologies, cement and steel manufacturers can adhere to regulatory demands while diminishing air pollution from their operations. Such measures are crucial not only for environmental conservation but also for the long-term viability and social responsibility of these industries, which are significant contributors to industrial emissions.
Future Trends in Gas Desulfurization for Enhanced Sustainability
Emerging technologies in gas desulfurization are set to transform the industry towards greater sustainability. Innovations such as biotechnological advances and the development of novel capture materials are proving promising. For instance, biological systems employing sulfur-oxidizing bacteria offer potential for higher efficiency and lower operational costs compared to conventional methods, as outlined in recent research.
Global regulatory trends are increasingly favoring stricter emissions standards, profoundly influencing gas desulfurization practices. Many countries are adopting more rigorous regulations that require industries to significantly reduce their emissions of sulfur compounds—a trend that encourages the deployment of advanced desulfurization technologies. This shift will potentially drive widespread adoption of cutting-edge solutions across multiple sectors.
The role of gas desulfurization in climate change mitigation cannot be overstated. Effective desulfurization processes directly contribute to lowering greenhouse gas emissions by removing sulfur compounds, which otherwise lead to acid rain and other environmental issues. By aligning with international climate goals, these processes not only support efforts to combat global warming but also pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable industrial future.
FAQ Section
What is gas desulfurization?
Gas desulfurization is the process of removing sulfur compounds, mainly sulfur dioxide (SO2), from gas streams in various industries to reduce air pollution and comply with environmental regulations.
Why is gas desulfurization important?
Gas desulfurization is crucial because it significantly decreases sulfur dioxide emissions, which are harmful to the environment and human health. It helps reduce acid rain and improve air quality.
What industries commonly use gas desulfurization?
Industries such as power generation, oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, cement, and steel frequently utilize gas desulfurization technologies to minimize sulfur emissions.
What are the challenges of implementing gas desulfurization technologies?
The main challenges include high installation and operational costs, technological complexities, and the need to adhere to evolving regulatory standards.
What future trends are expected in gas desulfurization?
Future trends include the adoption of biotechnological methods and novel capture materials, as well as the influence of stricter global emissions regulations promoting advanced desulfurization technologies.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Gas Desulfurization: A Pathway to Sustainability
- Benefits of Gas Desulfurization for Sustainability
- Technologies Employed in Gas Desulfurization Processes
- Challenges Faced in Gas Desulfurization Implementation
- Real-World Applications of Gas Desulfurization
- Future Trends in Gas Desulfurization for Enhanced Sustainability
- FAQ Section